std::ref 是 C++ 标准库中的一个工具,用于将对象封装为引用包装器 ,从而实现将原本作为值传递、需要拷贝的对象,能够以避免对象拷贝的方式传递。
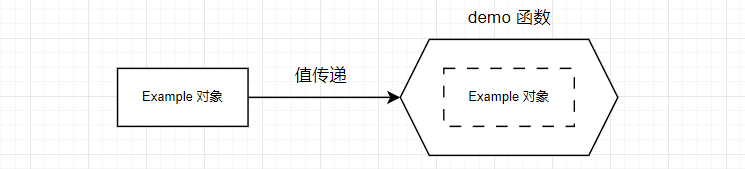
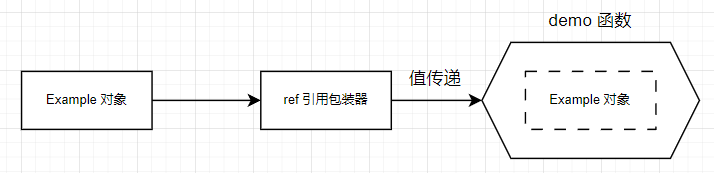
问题场景:一个对象传递一个以值方式接受参数的函数里,如何避免对象拷贝。
对于上述场景,主要发生在函数模板或者类模板中的参数传递。对于普通函数、类,如果函数设计为值传递,那么就是值传递,很难改变其传递方式。
注意:名字虽然叫做引用包装器,本质并不是引用,而是一种避免对象拷贝的技术、工具。
1. 问题场景
我们接下来复现提到的场景。
struct Example
{
Example()
{
data = new int[1000];
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
data[i] = i;
}
cout << "Example 构造函数" << endl;
}
Example(const Example& ex)
{
data = new int[1000];
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
data[i] = ex.data[i];
}
cout << "Example 拷贝构造" << endl;
}
void show_example()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
cout << data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
~Example()
{
if (data != nullptr)
{
delete[] data;
data = nullptr;
}
}
int* data;
};
#if 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "example.h"
template<class T>
void demo(T val)
{
func(val);
}
void func(Example& ex)
{
ex.show_example();
}
void test()
{
Example example;
// 只能以值方式传递,对象会发生拷贝
demo(example);
}
int main()
{
test();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
2. 解决思路
当一个对象以值方式传递给目标函数时,通常会发生拷贝操作。然而,我们可以通过设计一个对象包装器来实现对象的间接传递,从而在不进行拷贝的情况下将对象传递给目标函数。
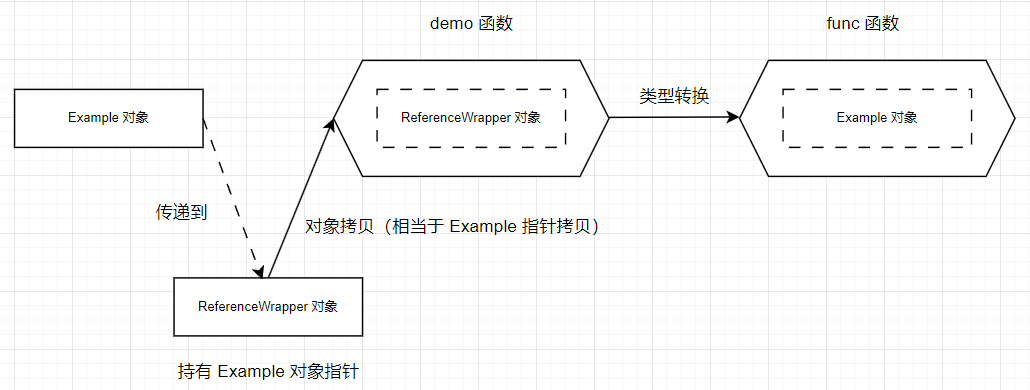
#if 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"example.h"
template<class T>
void demo(T val)
{
func(val);
}
void func(Example& ex)
{
ex.show_example();
}
// 构造包装器,将对象间接传递到 demo 函数中
struct ReferenceWrapper
{
ReferenceWrapper(Example& ex)
{
ptr = addressof(ex);
}
operator Example&()
{
return *ptr;
}
Example* ptr;
};
ReferenceWrapper my_ref(Example& ex)
{
return ReferenceWrapper(ex);
}
void test()
{
Example example;
//demo(example);
// 使用自定义 my_ref 包装器
demo(my_ref(example));
// 使用标准库 ref 引用包装器
demo(ref(example));
}
int main()
{
test();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
3. 应用举例
我们从 reference_wrapper 的实现中可以看到,std::ref 可以 应用到普通对象,也可以应用到函数对象,目的是确保在传递过程中不进行对象拷贝。接下来,让我们通过一个例子来了解什么场景下需要对普通对象或者函数对象使用 std::ref 引用包装器。
#if 1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<functional>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#include "example.h"
// 1. 对普通对象使用引用包装器
void demo(int num, Example& ex)
{
ex.show_example();
}
void test01()
{
Example example;
auto func = bind(demo, placeholders::_1, ref(example));
}
// 2. 对可调用对象使用引用包装
struct VectorCallBack
{
void operator()(int& v)
{
cout << v << endl;
++times;
}
int times{0};
};
void test02()
{
vector<int> vec{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// 可调用对象有自己的状态
VectorCallBack vcb;
for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), ref(vcb));
cout << "调用次数:" << vcb.times << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif


 冀公网安备13050302001966号
冀公网安备13050302001966号