门控循环单元(Gated Recurrent Unit, GRU)是一种改进的循环神经网络(RNN)架构,旨在解决传统 RNN 在处理长序列时面临的梯度消失问题。GRU 由 KyungHyun Cho 等人在2014年提出,其设计更加简洁,与长短期记忆网络(LSTM)相比,它减少了参数数量,并在许多应用中表现出色。
1. 算法原理
GRU 的核心思想是通过精巧设计的门控机制,使得模型能够更有效地捕捉序列数据中的长期依赖关系,从而在处理长序列数据时取得更好的性能。
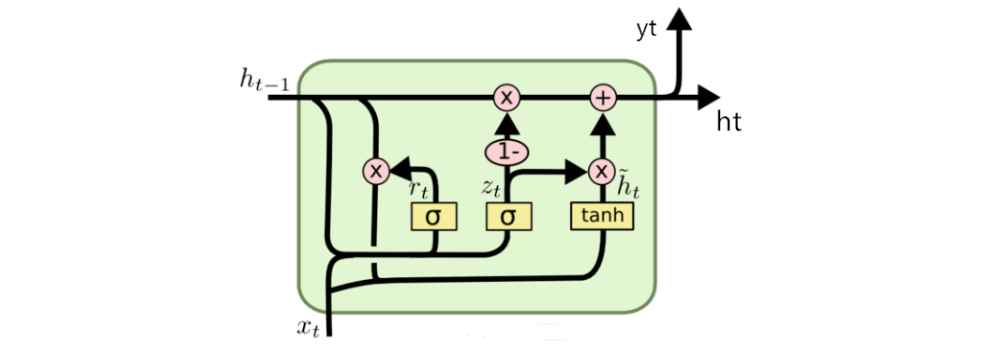
在 GRU 中,存在两个门控单来控制信息的流动:
- 重置门:控制如何组合新输入和先前的记忆
- 更新门:决定当前时刻的隐藏状态有多少部分由先前的隐藏状态和当前的候选隐藏状态来更新
相关计算公式如下:
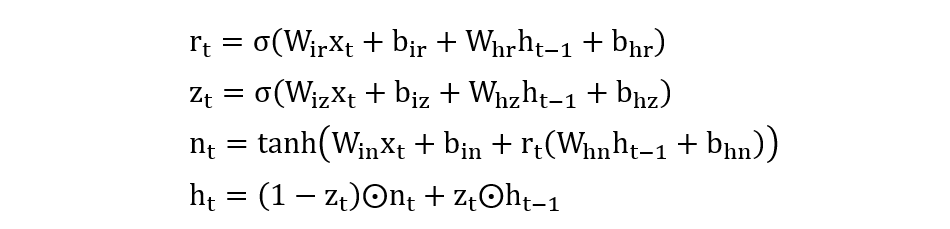
2. 算法使用
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def test01():
torch.manual_seed(42)
gru = nn.GRU(input_size=2, hidden_size=4, num_layers=1, bidirectional=False)
# 输入数据 (seq_len. batch_size, dim)
inputs = torch.rand(3, 1, 2)
# output: 每个时间步的隐藏状态
# hn: 最后一个时间步的隐藏状态
output, hn = gru(inputs)
print(output)
print(hn)
def test02():
torch.manual_seed(42)
gru = nn.GRUCell(input_size=2, hidden_size=4)
# 输入数据
inputs = torch.rand(3, 1, 2)
# 初始化隐藏状态
hn = torch.zeros(1, 4)
# 计算每个时间步
for data in inputs:
hn = gru(data, hn)
# 最后一个时间步的隐藏状态
print(hn)
if __name__ == '__main__':
test01()
print('-' * 70)
test02()
程序输出结果:
tensor([[[ 0.2018, -0.1158, -0.0443, -0.1317]],
[[ 0.1535, -0.1658, -0.0073, -0.2280]],
[[ 0.1685, -0.1421, 0.0186, -0.1869]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
tensor([[[ 0.1685, -0.1421, 0.0186, -0.1869]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
tensor([[ 0.1685, -0.1421, 0.0186, -0.1869]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)


 冀公网安备13050302001966号
冀公网安备13050302001966号