伯努利朴素贝叶斯(Bernoulli Naive Bayes)分类器是一种基于贝叶斯定理的概率分类器,常用于处理文本分类等离散数据。它假设特征之间是条件独立的,并且每个特征都遵循伯努利分布,即每个特征只有两个可能的取值(通常是0和1,表示特征是否出现)。
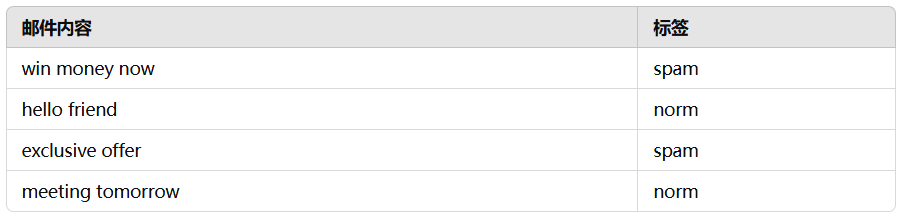
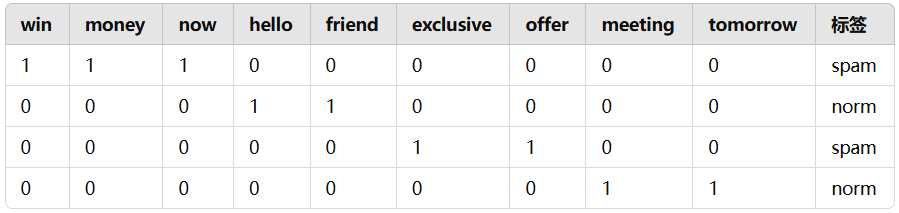
win,money,now,hello,friend,exclusive,offer,meeting,tomorrow,Spam 1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1 0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0 0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0
1. 伯努利分布
伯努利分布是一种离散概率分布,用于描述一个只有两个可能结果的随机试验。这两个结果通常被标记为 “成功”(记为1)和”失败”(记为0),并且成功的概率记为 p,失败的概率则为 1−p。
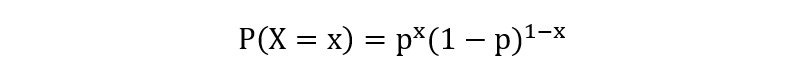
- \(p\) 是成功的概率, \(0 \leq p \leq 1\)
- x 是随机变量 X 的取值(0 或 1)
2. 训练过程
对于朴素贝叶斯算法,训练过程就是在根据训练数据,统计每个特征值的在类别条件下的概率,以及类别的先验概率。
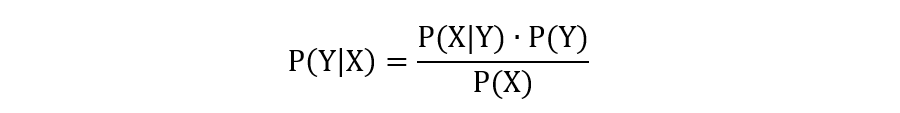
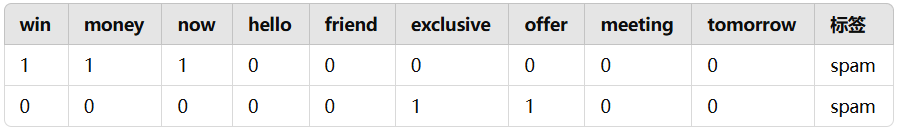
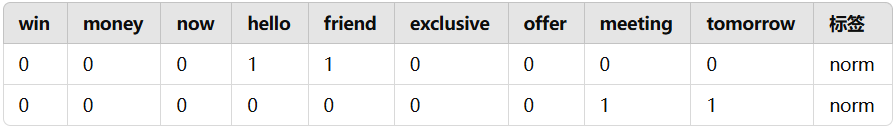
在伯努利朴素贝叶斯中,假设每个特征值服从伯努利分布。对于特征 x 在类别 y 条件下的概率计算,可以表示为:

公式中的 α 为拉普拉斯平滑系数,避免出现为 0 的情况,默认值为 1。训练得到的内容如下:x = 1 的条件概率:
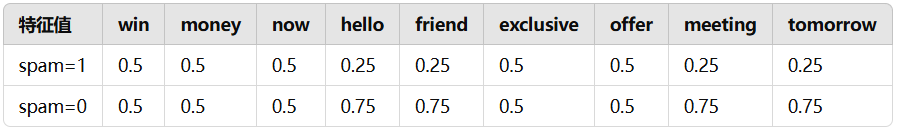
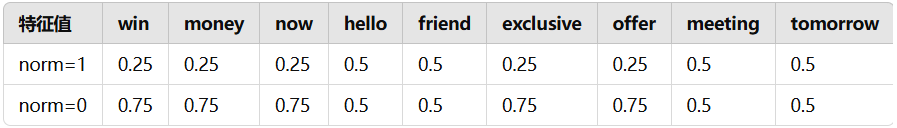
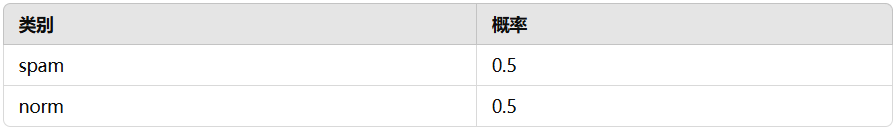
3. 预测过程
待预测的邮件内容: “win hello” ,二值向量表示:

3.1 计算 spam 分数
计算联合条件概率:
\(P(spam)·P(win=1∣spam) ⋯ P(tomorrow=0∣spam)\)转换为联合对数概率计算(避免数值溢出):
\(log(P(spam)) + log(P(win=1∣spam)) + ⋯ +log(P(tomorrow=0∣spam))\)代入样本计算最后的结果:
\(log(0.5) + log(0.5) + log(0.5) + log(0.5) +log(0.25) + \\log(0.75) + log(0.5) +log(0.5) + log(0.75) + log(0.75) = -6.40822366\)3.2 计算 norm 分数
计算联合条件概率:
\(P(norm)·P(win=1∣norm) ⋯ P(tomorrow=0∣norm)\)转换为联合对数概率计算:
\(log(P(norm)) + log(P(win=1∣norm)) +⋯ +log(P(tomorrow=0∣norm))\)代入样本计算最后的结果:
\(log(0.5) + log(0.25) + log(0.75) + log(0.75) +log(0.5)+\\log(0.5)+log(0.75)+log(0.75)+log(0.5)+log(0.5) =-6.00275855 \)由于 \(-6.00275855 > -6.40822366\),所以该邮件为 norm。
4. API 使用
from sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
# 训练
# alpha 平滑系数
# binarize 二值化阈值
estimator = BernoulliNB(alpha=1, binarize=0.0)
estimator.fit(data.iloc[:, :-1], data.iloc[:, -1])
print('对数先验概率:\n', estimator.class_log_prior_)
print('对数条件概率(值=1):\n',estimator.feature_log_prob_)
# 预测
new = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
scores = estimator.predict_joint_log_proba(new)
print('类别分数:', estimator.classes_, scores.squeeze())
程序执行结果:
对数先验概率: [-0.69314718 -0.69314718] 对数条件概率(值=1): [[-1.38629436 -1.38629436 -1.38629436 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 -1.38629436 -1.38629436 -0.69314718 -0.69314718] [-0.69314718 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 -1.38629436 -1.38629436 -0.69314718 -0.69314718 -1.38629436 -1.38629436]] 类别分数: [0 1] [-6.00275855 -6.40822366]


 冀公网安备13050302001966号
冀公网安备13050302001966号